Building Resilient Supply Chains: Strategies for Navigating Disruptions and Ensuring Continuity
Table of Contents
- Building Resilient Supply Chains: Strategies for Navigating Disruptions and Ensuring Continuity
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, businesses are increasingly focused on ensuring that their supply chains can withstand disruptions. The concept of supply chain resilience is becoming critical for organizations looking to maintain operations amidst unforeseen events, such as natural disasters, pandemics, and geopolitical shifts. But what exactly is supply chain resilience, and why has it gained such prominence?
Supply chain resilience refers to the ability of a supply chain to anticipate, respond to, and recover from unexpected disruptions. It’s about having the agility to continue operations during times of crisis, while being adaptable enough to evolve and improve over time. This article will explore strategies for building and maintaining resilience in your supply chain, as well as how to integrate these strategies into your business operations.
By adopting resilient practices, companies can not only avoid the negative impacts of disruptions but can also capitalize on opportunities during times of change. Let’s dive into the fundamental elements of building a resilient supply chain and why it should be a top priority for organizations across industries.
II. Understanding Supply Chain Resilience
What is Supply Chain Resilience?
Supply chain resilience is the capacity of a supply chain to bounce back from disruptions while continuing to deliver goods and services efficiently. It’s a key differentiator for businesses that operate in an environment filled with uncertainty, market shifts, and sudden changes. Unlike traditional supply chains, which may be designed for efficiency and cost-cutting, resilient supply chains are built for agility, robustness, and adaptability.
Resilience vs. Robustness vs. Agility
It’s important to understand the differences between resilience, robustness, and agility in supply chains.
- Resilience is about recovering from disruptions—whether minor or severe—without causing long-term damage to operations.
- Robustness refers to the ability to withstand shocks or disruptions in the first place, often through redundancy and backup systems.
- Agility is the ability to quickly adapt to new challenges or shifts in the market, such as changes in consumer behavior or raw material availability.
Together, these three attributes form the backbone of a resilient supply chain, ensuring that businesses can not only withstand disruptions but also recover quickly and thrive in an ever-changing landscape.
Statistics on Resilience
A study by the Business Continuity Institute found that 73% of organizations experienced some form of supply chain disruption over the past year. However, businesses that implemented resilient strategies reported a 40% higher likelihood of maintaining operations during crises. This statistic underscores the importance of investing in resilience-building measures.
Case Study: The Suez Canal Blockage
The Suez Canal blockage in 2021 highlighted the vulnerabilities in global supply chains. Companies that had implemented resilient strategies, such as alternative shipping routes or diversified supplier networks, were able to mitigate the impact of the blockage more effectively than those with rigid, centralized supply chains.
III. Key Strategies for Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience
A. Diversifying Suppliers and Sourcing Strategies
One of the foundational strategies for enhancing resilience is diversifying suppliers and sourcing strategies. Relying on a single supplier or geographic region for critical materials increases vulnerability. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic revealed how global supply chains reliant on specific regions, like China, could be disrupted, leaving companies scrambling for alternatives.
By building relationships with multiple suppliers and exploring nearshoring or onshoring options, businesses can mitigate risks associated with long-distance sourcing. In addition, dual sourcing—having more than one supplier for the same product—ensures that if one supplier faces a disruption, the other can step in to fulfill the order.
B. Implementing Advanced Risk Management Practices
Effective risk management is at the core of building resilient supply chains. Businesses must continuously monitor risks and assess potential threats to their operations. This is where big data analytics and predictive modeling come into play. By analyzing past events, market trends, and risk factors, companies can develop contingency plans and respond proactively to emerging threats.
Risk management isn’t just about identifying potential disruptions; it’s about understanding their financial, operational, and reputational impacts. This allows businesses to prioritize which risks to address first and how to allocate resources most effectively.
C. Building Inventory Buffers and Flexible Logistics
Another critical strategy is building inventory buffers and creating flexible logistics solutions. Having a safety stock of critical items—especially in industries like manufacturing or pharmaceuticals—helps absorb the shock of supply disruptions. It’s essential to balance inventory buffers with the cost of carrying excess stock, but the key is having dynamic inventory management that can adjust to market demand fluctuations.
Additionally, ensuring that logistics are flexible enough to handle disruptions is important. Cross-docking, using multiple distribution centers, and leveraging flexible transportation options are all ways to ensure that supply chains can remain fluid and responsive when disruptions occur.
IV. Technological Innovations Supporting Resilience
A. Leveraging Big Data and Analytics
Big data and analytics are transforming the way businesses approach supply chain resilience. With real-time data, businesses can predict demand more accurately, identify potential risks, and track shipments throughout the process. Companies that use predictive analytics can anticipate supply chain disruptions before they happen and take preventive measures.
By analyzing historical trends, weather patterns, geopolitical events, and other factors, predictive tools can help companies develop more accurate demand forecasts, manage inventory efficiently, and adjust quickly to changing conditions.
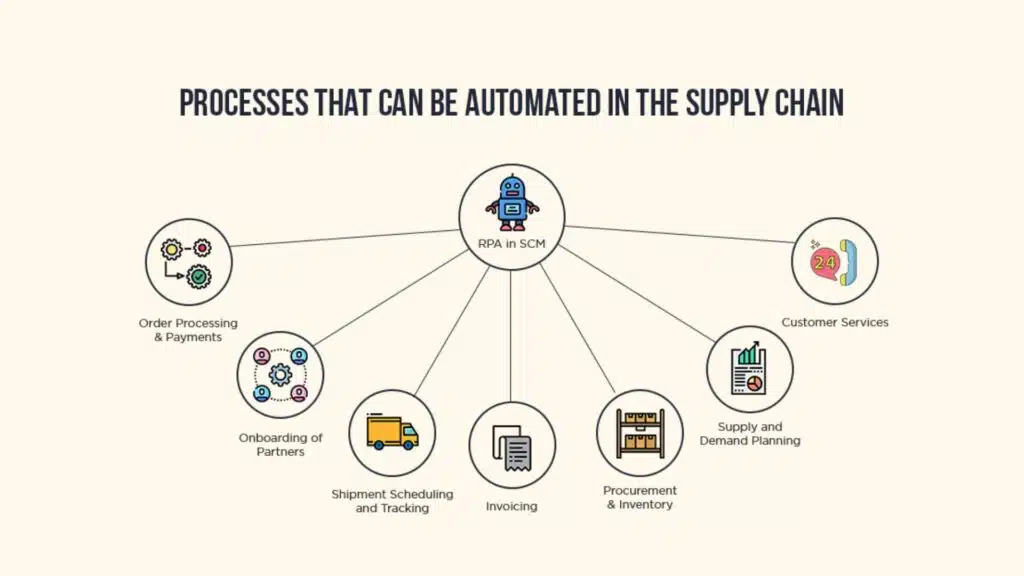
B. Implementing Automation and AI in Supply Chains
Another technological breakthrough that supports supply chain resilience is the use of automation and artificial intelligence (AI). Robotic Process Automation (RPA), AI-driven forecasting, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices can provide real-time tracking and monitoring of goods in transit, offering valuable insights for decision-making.
For example, AI-powered supply chain software can predict shortages or delays based on changing conditions, allowing businesses to adjust orders or reroute shipments on the fly. Automation also reduces human error and speeds up processes, increasing efficiency while improving resilience.
V. Organizational Culture and Leadership in Resilience
Building a Resilient Culture
A resilient supply chain isn’t just about technology and processes; it also requires an organizational culture that prioritizes adaptability, communication, and collaboration. Business leaders must foster an environment that encourages flexibility and preparedness. Employees should be trained to respond to disruptions quickly and effectively, with clear lines of communication across departments.
Leadership’s Role in Building Resilience
Leadership plays a critical role in driving a resilience-first culture. A strong leadership team that prioritizes resilience, invests in risk management practices, and communicates openly with employees and stakeholders is better positioned to navigate disruptions successfully. Companies with leadership that values innovation and continuous improvement are better able to pivot during times of crisis.
VI. Measuring and Monitoring Resilience Performance
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
To measure supply chain resilience, businesses must establish KPIs that track performance during disruptions. Some useful KPIs include recovery time, cost of disruption, order fulfillment rates, and inventory turnover. Regularly assessing these metrics helps businesses evaluate their resilience and identify areas for improvement.
VII. Conclusion
Supply chain resilience is no longer optional; it’s a necessity in today’s interconnected, unpredictable world. By implementing the right strategies, leveraging technology, and fostering a culture of adaptability, businesses can build supply chains that thrive in the face of disruption. It’s time for companies to take proactive steps to strengthen their supply chain resilience and prepare for whatever the future holds.
VIII. FAQ’s
1. What are the first steps to assess my supply chain’s resilience?
Begin by identifying potential risks and assessing how your current supply chain would react to various disruptions. Use data and analytics to evaluate supplier reliability, logistics capacity, and inventory management practices.
2. How can small businesses implement resilience strategies effectively?
Small businesses can start by diversifying suppliers, creating contingency plans, and investing in flexible logistics options. Partnering with reliable logistics providers can also help improve overall supply chain resilience.
3. What role does technology play in enhancing supply chain resilience?
Technology, such as AI, big data, and automation, helps companies predict disruptions, optimize inventory, and improve real-time decision-making. These tools increase agility and reduce the impact of disruptions.
4. How do I balance cost with the need for resilience?
Balancing cost with resilience requires careful risk management and strategic decision-making. Companies should focus on cost-effective solutions, such as nearshoring, flexible logistics, and smart inventory management, to avoid overextending resources while maintaining resilience.
5. Can supply chain resilience lead to a competitive advantage?
Yes, businesses with resilient supply chains are better equipped to handle disruptions, minimize downtime, and capitalize on opportunities that others may miss, offering a clear competitive advantage.





